How Cancer Starts?
Cancer starts when cells in a part of the body start to grow out of control,resulting into the formation of tumors. Cancer cell growth is different from normal cell growth. Instead of dying, cancer cells continue to grow and form new, abnormal cells. Cancer cells can also invade (grow into) other tissues, something that normal cells can’t do. Growing out of control and invading other tissues are what makes a cell a cancer cell.
Cells become cancer cells because of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) damage. DNA is in every cell and it directs all its actions.People can inherit abnormal DNA (it’s passed on from their parents), but most often DNA damage is caused by mistakes that happen while the normal cell is reproducing or by something in the environment. Sometimes the cause of the DNA damage may be something obvious like cigarette smoking or sun exposure . But it’s rare to know exactly what caused any one person’s cancer.

Tumours
Tumours are of two types. BENIGN and MALIGNANT. Cancer cells often travel to other parts of the body where they can grow and form new tumors. This happens when the cancer cells get into the body’s bloodstream or lymph vessels. The process of cancer spreading is called metastasis.
No matter where a cancer may spread, it’s always named based on the place where it started. For example, colon cancer that has spread to the liver is called metastatic colon cancer, not liver cancer. In this case, cancer cells taken from the liver would be the same as those in the colon. They would be treated in the same ways too.
Benign tumours do not have the capacity to spread to other parts of the body whereas malignant tumours do possess ability to spread to other parts of the body. These malignant tumours are commonly termed as CANCER. In India, the number of newly diagnosed cancer cases is increasing and is expected to be more than 1 million by 2015. This is attributable to increasing tobacco and alcohol use, changing lifestyle and changing food habits.
Signs And Symptoms Of Cancer
- Lump on any part of the body.
- Non healing ulcer (more than 3 weeks) or white patch in the mouth.
- Hoarseness of voice.
- Difficulty in swallowing.
- Feeling of lump in the throat.
- Cough more than 3 weeks (Infection in the chest need to be ruled out).
- Change in the bowel habits.
- Blood in stools/black coloured stools.
- Jaundice with itching over the body.
- Blood in sputum & urine
Types Of Cancer
There are more than 200 types of cancers. Cancers are divided based on the organ from which they arise. For example – Lung cancer, esophageal cancer, colon cancer etc. Cancers can also be divided based on the cells from which they arise. Eg. Cancers arising from lining of tissues or organs are called carcinomas, cancers arising from connective tissues are called sarcomas.
Cancer Staging
Staging of the cancer is done to assess the extent of the cancer. Thus it gives information regarding the prognosis of the patient and also guides the doctors to determine the requirement of various treatment options available.
How Cancers Are Diagnosed?
To diagnose a cancer doctors do a biopsy for that particular part of the tumour where they remove a part or whole of the tumour tissue and send it to pathologist to see the part under microscope. This can be accomplished with the use of fine needle (FNAC), wide bore needle (trucut biopsy) or surgical procedure (Incision/excision biopsy). Accurate diagnosis of the type of cancer might need some special tests (immunohistochemistry/ tumour markers).
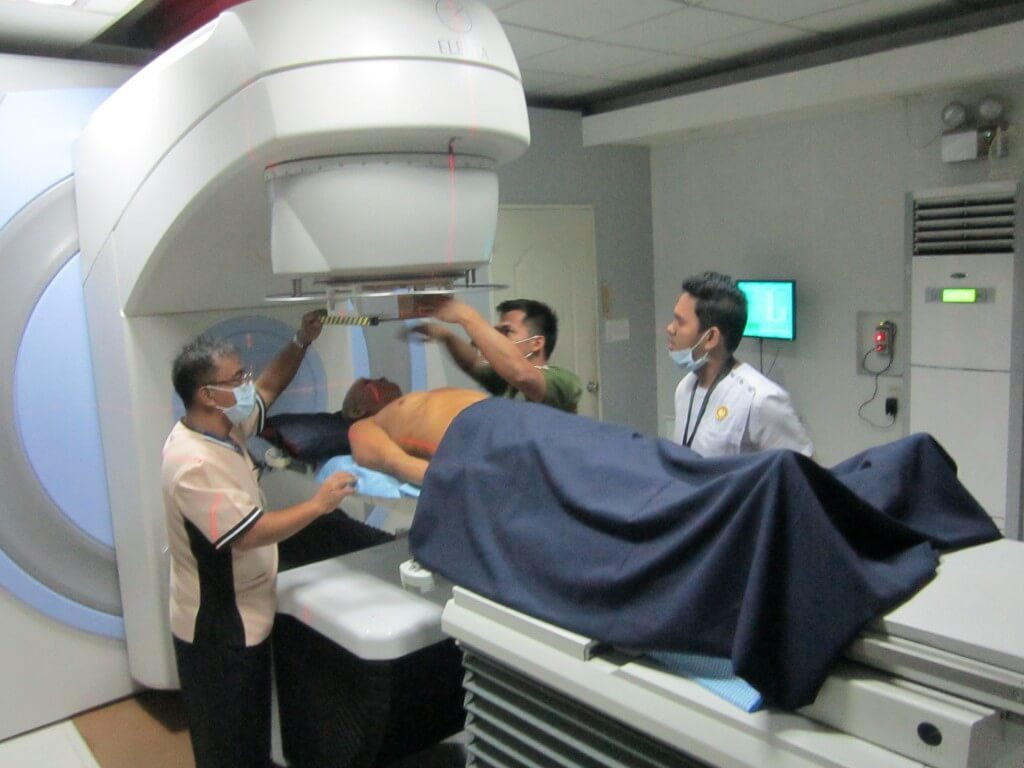
Treatment Of Cancer
3 major tools used by oncologists to treat a patient of cancer are surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy. The treatment for each of the cancer type varies based on the from which organ it arises, type of cancer and extent of cancer. In majority of the cancers, early stage tumours are usually treated by single modal
ity of the treatment where as more advanced tumours need all three forms of treatments.
Asian Cancer Institute is the best cancer hospital to provide cancer treatment and education in Mumbai with expertise cancer specialists.
Understanding Cancer Prognosis
Many factors can influence the prognosis of a person with cancer. Among the most important are the type and location of the cancer, the stage of the disease (the extent to which the cancer has spread in the body), and the cancer’s grade (how abnormal the cancer cells look under a microscope”an indicator of how quickly the cancer is likely to grow and spread).
Other factors that affect prognosis include the biological and genetic properties of the cancer cells (these properties, which are sometimes called biomarkers, can be determined by specific lab and imaging tests), the patient’s age and overall general health, and the extent to which the patient’s cancer responds to treatment.


